Become a Business Analyst
MS Excel | Power BI | SQL | Python
Add-Ons: Looker Studio and ChatGPT

Become a Data Analyst
MS Excel | Power BI | SQL | Python
Join our "Become a Business Analyst" course and master MS Excel, Power BI, SQL, and Python.
Through these 58 hours of classes, you'll gain the skills necessary to thrive in the competitive job market or launch a successful freelance career. Unleash your potential as a business analyst!
Module 0: Introduction to Business Analysis
Introduction to Business Analysis
• Definition and purpose of business analysis
• Importance of business analysis in various industries
• Key responsibilities of a Business Analyst
Understanding Business Requirements
• What are business requirements, and why are they essential?
• Types of requirements: Functional, non-functional, technical, and business
• Techniques for gathering requirements (e.g., interviews, surveys, workshops)
Tools and Techniques for Analysis
• Brief introduction to essential tools: MS Excel, Power BI, SQL
• Overview of visualization tools for data analysis (Power BI, Excel charts)
• Introduction to data processing techniques: Cleaning, structuring, and preparing data for analysis
Stakeholder Analysis and Communication
• Identifying and understanding stakeholders
• Techniques for effective communication with stakeholders
• Importance of collaboration in the analysis process
Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking
• Techniques for framing business problems
• Approaches to analyzing data and deriving insights
• Tips on making recommendations based on analysis
• Case Study Analysis
Module 1: Excel for Business Analysis
Introduction to Excel for Business Analysis
• Overview of Excel’s relevance in business analysis
• Introduction to the Excel interface, ribbons, and essential settings
• Best practices for data organization and data hygiene
Core Excel Formulas and Functions for Business Analysis
• Basic Functions: SUM, AVERAGE, COUNT, MIN, MAX, COUNTA, etc.
• Logical Functions: IF, AND, OR, IFERROR, IFS
• Lookup and Reference Functions: VLOOKUP, HLOOKUP, INDEX, MATCH, XLOOKUP (Excel 365)
• Text Functions: LEFT, RIGHT, MID, CONCATENATE, TEXTJOIN, LEN, FIND, TRIM, SUBSTITUTE
• Date & Time Functions: TODAY, NOW, DATE, YEAR, MONTH, DAY, NETWORKDAYS, EOMONTH
Data Cleaning and Preparation Using Power Query
• Introduction to Power Query and the ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) process
• Data Import: Importing data from various sources (CSV, databases, online data, etc.)
• Data Transformation:
o Remove duplicates
o Split and merge columns
o Data filtering and sorting
o Transposing data
• Data Transformation Advanced:
o Using "Group By" to summarize data
o Conditional columns and custom columns
o Unpivoting tables to prepare for analysis
Exploring and Analyzing Data with Pivot Tables and Pivot Charts
• Creating Pivot Tables:
o Building from scratch and automating updates
o Sorting, filtering, grouping, and summarizing data
• Pivot Charts: Integrating charts with pivot tables
• Slicers and Timeline Tools:
o Adding interactivity to pivot tables and pivot charts
Advanced Data Visualization with Charts and Dashboards
• Excel Charts:
o Types of charts and their business applications
o Formatting and customizing charts for storytelling
• Building Dashboards:
o Dashboard layout best practices
o Utilizing named ranges and dynamic ranges
o Adding interactivity with form controls (drop-downs, buttons)
o Creating KPI indicators with conditional formatting
• Dashboard Examples:
o Sales dashboards, performance scorecards, and executive summary dashboards
Automating Tasks and Enhancing Efficiency with Advanced Excel Tools
• Data Validation: Setting criteria, drop-down lists, and error messages
• Conditional Formatting:
o Highlighting critical data points
o Using formulas in conditional formatting for KPI indicators
• What-If Analysis:
o Goal Seek, Data Tables, Scenario Manager
• Data Protection and Collaboration:
o Locking cells, protecting sheets and workbooks
o Collaboration tools and sharing options in Excel
Module 2: Power BI for Business Analysis
Introduction to Power BI for Business Analysis
• Overview of Power BI: its role in business intelligence and analysis
• Key Components: Power BI Desktop, Power BI Service, and Power BI Mobile
• Introduction to the Power BI Desktop interface and key features
• Best practices in report design and data storytelling
Data Connection and ETL with Power Query
• Connecting to Data Sources:
o Importing data from various sources (Excel, SQL, Web)
o Data refresh options and settings
• Data Transformation:
o Data cleaning techniques (removing duplicates, handling nulls)
o Splitting, merging, and reformatting columns
o Unpivoting tables and managing nested data
• Advanced Data Transformation:
o Grouping, aggregating, and creating conditional columns
o Merging and appending queries for data consolidation
Data Modeling and Relationships in Power BI
• Building a Data Model:
o Understanding tables, fields, and relationships
o Designing a star schema and the importance of primary keys
• Creating Relationships:
o Managing one-to-one, one-to-many, and many-to-many relationships
Introduction to DAX for Advanced Calculations
• Understanding DAX (Data Analysis Expressions):
o Introduction to calculated columns, measures, and tables
• Basic DAX Functions:
o Aggregation functions (SUM, COUNT, AVERAGE)
o Logical functions (IF, AND, OR)
o Text and Date functions
• Intermediate DAX:
o Time Intelligence functions (DATEADD, DATESYTD, SAMEPERIODLASTYEAR)
o Iterative functions (SUMX, AVERAGEX)
o CALCULATE and FILTER for conditional calculations
Data Visualization and Charting in Power BI
• Creating Basic Visualizations:
o Bar, column, line, pie charts, and their usage in business analysis
o Card visualizations for displaying KPIs
o Formatting and customizing visuals
• Advanced Visualizations:
o Combo charts, scatter plots, treemaps, and waterfalls
o Map visualizations and geographic analysis
• Using Slicers and Filters:
o Adding slicers, filters, and bookmarks for interactivity
o Drill-through and cross-report filtering
Building Interactive Dashboards and Reports
• Dashboard Layout and Best Practices:
o Setting up dashboard themes, color schemes, and layouts
o Organizing KPIs and visual hierarchy
• Adding Interactivity:
o Syncing slicers across pages
o Designing buttons, tooltips, and page navigation
o Using drill-down and drill-up for exploring data at different levels
• Dashboard Case Studies:
o Sales dashboard, financial performance dashboard, and operational metrics dashboard
Power BI Service: Publishing, Sharing, and Collaboration
• Publishing to Power BI Service:
o Steps for publishing reports and understanding workspaces
o Setting up data refreshes and understanding refresh frequency limits
Advanced Analytics and AI Insights in Power BI
• AI Visuals:
o Using Q&A visuals for natural language questions
o Decomposition Tree for analyzing data breakdowns
o Key Influencers visual for identifying important factors
• Advanced Analytics:
o Forecasting and trend analysis in Power BI
Module 3: SQL for Business Analysis
Introduction to SQL for Business Analysis
• Overview of SQL and its role in data analysis
• Basic Database Concepts: tables, columns, rows, primary and foreign keys
• Types of SQL Databases (e.g., MySQL, SQL Server, PostgreSQL)
• Introduction to SQL IDEs (SQL Server Management Studio)
Basic SQL Querying
• SELECT Statement:
o Selecting specific columns and using aliases
• Filtering Data:
o WHERE clause for conditional selection
o Logical operators (AND, OR, NOT)
• Sorting Data:
o ORDER BY clause and sorting in ascending/descending order
Data Aggregation and Summarization
• Aggregate Functions:
o COUNT, SUM, AVG, MIN, MAX
• Grouping Data:
o GROUP BY clause and aggregate functions
• Filtering Grouped Data:
o HAVING clause to filter aggregated data
• Advanced Aggregates:
o Calculating percentages, ratios, and creating custom calculations
Working with Data Joins for Data Analysis
• Introduction to Joins:
o Understanding the purpose of joins in combining data
• Types of Joins:
o INNER JOIN, LEFT JOIN, RIGHT JOIN, FULL OUTER JOIN
• Self Joins and Cross Joins:
o Scenarios and examples for advanced join usage
• Combining Multiple Tables:
o Using multiple joins for complex data combinations
Data Manipulation (DML) for Data Maintenance
• Inserting Data:
o INSERT INTO for adding new records
• Updating Data:
o UPDATE command with conditions for modifying records
• Deleting Data:
o DELETE statement with filters to remove records
• Best Practices:
o Using transactions for safe updates and deletions
o COMMIT and ROLLBACK for transaction management
Data Analysis and Reporting
• Basic Data Analysis Techniques
• Descriptive Statistics
• Using SQL for Data Analysis
• Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
• Generating Reports
• Creating Simple Reports in SSMS
• Exporting Data to Excel
Module 4: Python for Business Analysis
Introduction to Python for Data Analysis
• Overview of Python:
o Python's role in data analysis and business intelligence
o Installing Python, Jupyter Notebook, and Anaconda environment setup
• Python Basics:
o Data types, variables, and basic syntax
o Operators, conditionals, loops, and functions
• Introduction to Jupyter Notebooks:
o Benefits and basic functionalities
Data Manipulation with Pandas
• Introduction to Pandas Library:
o DataFrames and Series as core data structures
• Data Importing:
o Loading data from CSV, Excel, and databases
o Exporting data to different file formats
• Data Cleaning and Transformation:
o Handling missing data, duplicates, and outliers
o Filtering, sorting, and conditional selections
• Data Aggregation and Grouping:
o Using groupby, pivot_table, and crosstab
o Aggregating and summarizing data for business insights
Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) with Python
• Basic Descriptive Statistics:
o Calculating mean, median, mode, standard deviation
• Data Visualization for EDA:
o Using Pandas plotting methods for quick insights
o Using Matplotlib and Seaborn for basic plotting (histograms, boxplots, scatter plots)
• Data Distributions and Correlations:
o Identifying data distributions and patterns
o Calculating and visualizing correlations
Advanced Data Manipulation Techniques
• Advanced Data Cleaning:
o Regular expressions for data cleaning (e.g., text data)
o Data type conversions and date manipulations
• Merging and Joining Datasets:
o Combining data from multiple sources using merge, concat, and join
Data Visualization for Business Reporting
• Introduction to Matplotlib and Seaborn:
o Creating line, bar, and scatter plots for insights
• Advanced Visualization Techniques:
o Box plots, pair plots, heatmaps, and joint plots
• Customizing and Styling Visuals:
o Adding titles, labels, legends, and customizing aesthetics
• Case Studies:
o Visualization techniques in business reports (e.g., sales trends, customer segmentation)
Working with Date and Time Data
• Introduction to DateTime in Python:
o Using the datetime module and Pandas DateTime features
Data Analysis with Numpy
• Understanding Numpy:
o Numpy arrays and basic operations
• Statistical and Mathematical Operations:
o Mean, median, mode, standard deviation, and correlation
• Matrix Operations for Business Applications:
Add-Ons: Looker Studio for Business Analysis
Introduction to Looker Studio
• Overview of Looker Studio:
o Understanding Looker Studio’s role in data analysis and visualization
o Key features: connectors, visualizations, and interactivity
• Looker Studio Interface Walkthrough:
o Overview of the dashboard interface and navigation
o Key tools and panels for chart creation, customization, and layout management
• Connecting to Data Sources:
o Using connectors for Google Sheets, BigQuery, SQL databases
Data Preparation and Transformation
• Data Source Configuration:
o Configuring data fields, field types, and data labels
• Data Transformation:
o Creating calculated fields for new insights
o Applying data blending to integrate multiple data sources
• Aggregations and Calculations:
o Calculating sums, averages, ratios, and other KPIs
o Using basic math functions and conditional calculations
Introduction to Visualizations and Basic Charts
• Chart Types and Their Uses:
o Overview of common chart types: bar, line, pie, and scatter plots
• Setting Up Basic Charts:
o Adding charts to the canvas and configuring data settings
o Adjusting chart properties like dimensions, metrics, and labels
• Using Filters and Controls:
o Adding interactive controls: date range selectors, drop-down filters
o Configuring filters to allow users to interact with data dynamically
Building Interactive Dashboards
• Designing for Interactivity:
o Arranging layouts and using themes for better user experience
• Adding User Controls:
o Date range controls, filter controls, and data drill-downs
Sharing, Publishing, and Collaboration
• Publishing Reports:
o Setting up sharing permissions and publishing options
o Embedding reports on websites or in other platforms
Add-Ons: ChatGPT for Business Analyst
Introduction to ChatGPT and AI Language Models
• Understanding ChatGPT:
o Overview of ChatGPT, its functionalities, and use cases in business
o Role of AI in augmenting business analysis: data processing, reporting, and insight generation
• Ethical Considerations and Limitations:
o Understanding data privacy, bias, and limitations of AI-generated content
• Accessing ChatGPT:
o Navigating ChatGPT on the web and using the OpenAI API for advanced functionalities
Using ChatGPT for Data Exploration and Summarization
• Data Summarization Techniques:
o Generating quick summaries of datasets, reports, and articles
o Asking ChatGPT specific questions to get concise summaries
• Interpreting Large Datasets:
o Techniques for summarizing trends and identifying outliers
o Extracting key insights from structured and unstructured data
• Creating Automated Data Briefs:
o Setting up ChatGPT prompts to produce daily, weekly, or monthly data briefs
o Best practices for using ChatGPT to monitor trends and changes
Leveraging ChatGPT for Scenario Analysis and Forecasting
• Scenario Analysis Basics:
o Using ChatGPT to generate and evaluate different business scenarios
• Forecasting and Trend Analysis:
o Leveraging historical data to ask predictive questions and forecast trends
In today’s data-driven world, business analysis skills have become essential across industries. Business Analysts (BAs) are now expected to harness the power of tools like Excel, Power BI, SQL, Python, Looker Studio, and ChatGPT to analyze, visualize, and communicate data-driven insights. At AIN GenX, our comprehensive Business Analysis training combines these in-demand tools to help learners master the art of analysis and make informed decisions that drive value.
1. Excel for Foundation and Beyond
Excel is the bedrock of business analysis. It’s simple yet powerful, offering BAs the ability to clean data, calculate metrics, and create pivot tables. Through AIN GenX’s training, learners master advanced Excel functions, dashboard design, and Excel BI skills that are crucial for analyzing data efficiently and creating intuitive reports.
2. Power BI for Dynamic Data Visualization
Power BI empowers business analysts to transform raw data into visually engaging and interactive dashboards. AIN GenX guides learners in developing insightful dashboards that are not only visually appealing but also deliver actionable insights at a glance. With Power BI, trainees learn to connect multiple data sources, build KPIs, and make data accessible to stakeholders.
3. SQL for Deep Data Exploration
SQL is the language of databases and a must-have skill for business analysts who want to work with structured data. At AIN GenX, we provide hands-on training in SQL to help learners query data, join datasets, and perform in-depth analysis. SQL skills empower BAs to access, manipulate, and extract the exact information they need to address business questions directly from databases.
4. Python for Data Analysis and Automation
Python offers advanced analytics and automation capabilities, making it a game-changer for business analysts. With Python training at AIN GenX, learners dive into data cleaning, statistical analysis, and automation using libraries like Pandas and Matplotlib. Python skills open the door to data manipulation and provide deeper insights than traditional tools.
5. Looker Studio for Custom Reporting
Looker Studio (formerly Google Data Studio) is essential for creating custom reports that are easy to share and interact with online. AIN GenX covers Looker Studio’s functionalities in data blending, calculated fields, and interactive reporting. Learners gain the skills to create branded, professional reports that convey the right story to stakeholders.
6. ChatGPT for Streamlining Analysis and Reporting
Generative AI tools like ChatGPT are revolutionizing business analysis by automating routine tasks, from generating report summaries to scenario planning. At AIN GenX, we introduce ChatGPT as a productivity partner, showing analysts how to craft effective prompts for data queries, summaries, and report generation. ChatGPT saves time and enhances the clarity of analysis, allowing analysts to focus on strategy.
Why Choose AIN GenX?
AIN GenX stands out because of our commitment to real-world application and hands-on experience. Our training doesn’t just cover tool functionalities; it focuses on how these tools work together to solve complex business problems. With a curriculum designed by industry experts, interactive sessions, and practical projects, AIN GenX empowers learners to build confidence and start making an immediate impact in their roles.
The beauty of business analysis is that it draws from various skills and can be applied across a wide range of industries. Consequently, the eligibility criteria are often broad, accommodating both beginners and professionals from diverse fields. Here are the primary eligibility factors that help determine if someone is ready for Business Analyst training:
1. Educational Background
○ Preferred: A bachelor’s degree in business, finance, IT, data science, economics, or related fields is beneficial as it provides foundational knowledge in areas relevant to business analysis.
○ Non-Specific: Many business analyst training programs welcome individuals from non-business backgrounds (such as engineering, humanities, or science) who are looking to transition into a data-focused role.
2. Basic Analytical Skills
○ Analytical Mindset: A natural inclination for problem-solving and analytical thinking is essential. This includes the ability to approach problems methodically and interpret data logically.
○ Quantitative Aptitude: While business analysts may not need advanced math, a good grasp of numbers, statistics, and quantitative thinking is helpful.
3. Computer Literacy
○ Essential: Basic computer skills are necessary, especially familiarity with Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets.
○ Advantageous: Prior exposure to any analytical tools (such as SQL, Power BI, or Python) is helpful but not mandatory. Most training programs, like those at AIN GenX, start from foundational levels, making it suitable for beginners.
4. Interest in Data and Technology
○ Data-Driven Mindset: A genuine interest in working with data, analyzing trends, and using insights for decision-making.
○ Open to Learning: Since business analysis relies heavily on tools like Power BI, SQL, and Python, a willingness to learn these technologies is important.
5. Communication and Soft Skills
○ Business analysts must often interpret data for non-technical stakeholders, so strong communication and presentation skills are valuable.
○ Collaborative Skills: Experience working in team environments is beneficial since analysts frequently work across departments.
1. High Demand and Job Opportunities
Business analysis is an in-demand field with applications in multiple industries, from finance and healthcare to technology and retail.
Business analysts are key in data-driven decision-making, making them highly valuable to companies that rely on data insights.
As organizations prioritize data analysis for strategic decisions, certified business analysts enjoy robust career growth and job stability.
2. Competitive Salary Potential
Business analysts are well-compensated due to their specialized skill set. According to industry salary surveys, business analysts can earn competitive salaries with the potential for significant increases based on experience and skill level.
Additional skills in tools like SQL, Power BI, Python, and advanced Excel further enhance earning potential.
3. Improved Data-Driven Decision Making
Business analysts help organizations make decisions based on data rather than intuition. Through training, analysts learn how to extract, interpret, and present data insights effectively.
This empowers organizations to enhance efficiency, identify opportunities, and optimize operations.
4. Mastery of Essential Tools and Techniques
Business Analyst training covers a range of essential tools, such as Excel, SQL, Power BI, Looker Studio, Python, and even generative AI like ChatGPT.
Training in these tools enhances your technical skill set, enabling you to handle complex data, create insightful visualizations, automate repetitive tasks, and streamline reporting processes.
5. Enhanced Problem-Solving Skills
Business Analyst training sharpens analytical and problem-solving abilities. It teaches you how to identify issues, gather relevant data, and use structured approaches to find solutions.
These problem-solving skills are valuable for tackling business challenges, leading to better project outcomes and optimized processes.
6. Cross-Functional Collaboration and Communication
Business Analysts work across departments, making them central to team collaboration. Training in this field enhances skills in communicating technical data insights to non-technical stakeholders, bridging the gap between departments.
Strong communication and storytelling abilities are built during training, enabling analysts to make data actionable and understandable for all team members.
7. Industry Versatility and Transferable Skills
Business Analyst skills are transferable across multiple industries and functions. Whether it’s healthcare, finance, technology, or logistics, business analysis provides versatile skills that can adapt to various roles and industries.
Skills in data analysis, data visualization, and business intelligence are widely applicable, enhancing job flexibility and mobility.
8. Career Advancement and Strategic Role Development
Business analysts often play a strategic role, contributing to company growth and development by offering insights that inform major business decisions.
With experience, business analysts can advance to roles such as data analyst, project manager, product manager, or even C-suite positions. Many analysts move on to specialize further, becoming leaders in data science, business intelligence, or strategy.
9. Hands-On Experience with Real-World Data
Many Business Analyst training programs, like those offered at AIN GenX, provide hands-on projects that use real-world data. This enables learners to apply their skills in practical scenarios, ensuring that they are job-ready upon course completion.
Real-world data exposure builds confidence, making the transition to workplace projects smoother.
10. Continuous Learning and Adaptability in the Field
Business Analyst training fosters adaptability and continuous learning. As data tools and methods evolve, trained analysts can easily adapt to new software, techniques, and trends in the data field.
This flexibility ensures that business analysts remain relevant and capable of meeting new challenges, making them valuable long-term assets to any organization.
1. Diverse Career Opportunities Across Industries
High Demand Across Sectors: Business analysis skills are essential in industries like finance, healthcare, technology, retail, logistics, and consulting. This diversity allows analysts to choose from a range of fields based on their interests.
Versatile Job Roles: Business analysts can transition into specialized roles like data analyst, financial analyst, product analyst, systems analyst, and project manager, or move into leadership positions such as BI manager or strategy consultant.
2. Bridging Business and Technology
Essential Role in Digital Transformation: Business Analysts are critical for guiding digital transformation, ensuring that companies adapt to new technologies and optimize their processes for digital platforms.
In-Demand Technical Skills: Training in tools like Excel, SQL, Power BI, Python, and ChatGPT provides the technical foundation needed to succeed in today’s digital landscape, enabling analysts to work efficiently with both business and IT teams.
3. Growth in Data-Driven Decision Making
Increasing Reliance on Data: Businesses are placing greater emphasis on data to understand customer behavior, forecast trends, and optimize operations, all of which require skilled business analysts.
Role in Data Interpretation and Communication: Business analysts translate complex data insights into actionable strategies, helping companies harness data to make smarter, evidence-based decisions.
4. Strategic Impact and Influence
Decision-Making Partner: Business analysts play an integral role in strategic decision-making, helping companies set goals, identify areas for improvement, and create sustainable growth strategies.
Influence on Business Strategy: Business analysts provide insights that impact high-level decision-making, contributing to areas such as resource allocation, cost reduction, process improvement, and customer satisfaction.
5. Adaptability and Flexibility
Transferable Skills: The skills gained through Business Analyst training, like problem-solving, data analysis, and visualization, are adaptable across various roles and industries. This flexibility means analysts can switch fields or roles with ease.
Advancement and Specialization: Experienced business analysts can specialize further in areas like business intelligence, data science, or project management, or move into roles that focus on analytics, technology, and strategy.
6. Enhanced Earnings Potential
Competitive Salaries: Business analysts are among the better-compensated professionals, with salary potential increasing as they gain experience and develop expertise in advanced tools and techniques.
Skills Premium: Knowledge of advanced tools like Power BI, Python, and machine learning can significantly boost an analyst's market value and earning potential.
7. International Opportunities and Remote Work Potential
Global Demand for Analysts: Skilled business analysts are in demand worldwide, providing opportunities to work in international markets or secure remote roles with companies in various locations.
Freelancing and Consulting: Many business analysts choose to freelance or consult, offering flexibility and autonomy over their work while helping multiple organizations improve their data practices.
8. Continuous Learning and Career Longevity
Scope for Lifelong Learning: As technology and data practices evolve, so does the scope for continuous skill development in business analysis. Learning new tools and techniques like AI-driven analysis, advanced data visualization, or specialized data languages keeps analysts current.
Future-Ready Skills: Training in generative AI tools like ChatGPT positions analysts to integrate AI insights into their workflows, ensuring they stay ahead in a rapidly evolving job market.
What is Business Analysis?
Business analysis involves identifying business needs, analyzing processes, and providing data-driven recommendations to improve performance. Business analysts act as a bridge between stakeholders and IT, ensuring that solutions meet business requirements.
Who should pursue Business Analyst training?
Business Analyst training is ideal for professionals seeking to transition into data-driven roles, recent graduates in relevant fields, and existing professionals in finance, IT, operations, or management who wish to enhance their analytical skills.
What skills will I learn during Business Analyst training?
Training typically covers skills such as data analysis, data visualization, requirement gathering, stakeholder communication, proficiency in tools like Excel, Power BI, SQL, Python, and Looker Studio, and techniques for problem-solving and decision-making.
What are the prerequisites for Business Analyst training?
While there are no strict prerequisites, a basic understanding of business concepts, some familiarity with Excel, and a willingness to learn data analysis tools are beneficial. Many programs start with foundational concepts to accommodate all learners.
What tools and software will I learn?
Business Analyst training often includes tools such as Microsoft Excel, Power BI, SQL, Python, Looker Studio, and ChatGPT. These tools help in data analysis, visualization, and automation, equipping analysts with the necessary skills to excel in their roles.
How can Business Analyst training enhance my career prospects?
Business Analyst training provides you with in-demand skills that are valuable across industries, improving your job prospects, increasing earning potential, and opening doors to various roles and career advancement opportunities.
Is certification available upon completion of the training?
Successful participants will get the AIN GenX and Skill Development Council Karachi certificates.
Instructor
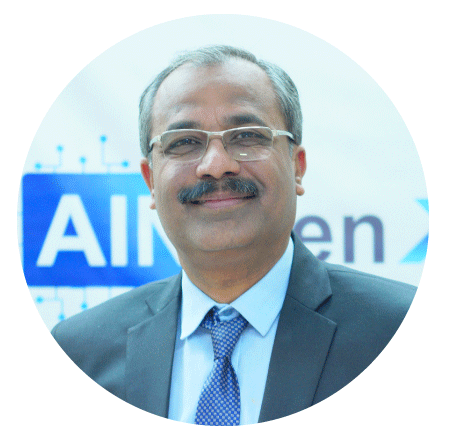

Irfan Bakaly
Data Analyst
25+ years of experience in Data Analysis

Noor Surani
Tech Entrepreneur
25+ years of experience in Data Analysis

Amynah Reimoo
Data Analyst
2+ years of experience in Data Analysis

Tamkeen Ahmed
Data Analyst
Supply Chain Profession
5+ years of Teaching Experience
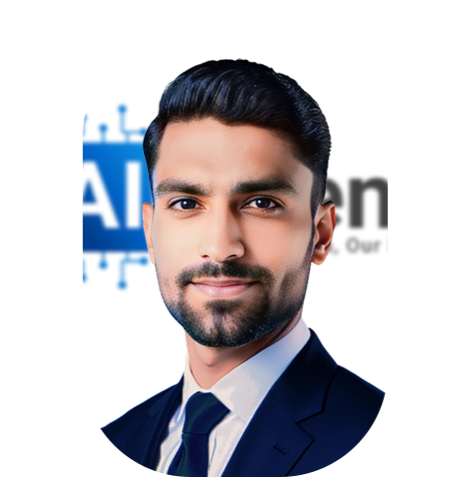

Sohail Ahmed
Data Scientist
5+ years of experience
in Data Science
Who this course is for:
Business Analyst
Duration
● 2 Months (58 Hours)
Classes
● Online via Zoom
Schedule
- Days: Mon, Wed & Fri
- Timing: 07:30 - 09:30 PM (PST)
Starting From
● 15 November, 2024
Course Fee
● Online
Rs. 12,000/- (one time payment)
● Excluding the SDC Certificate Fee
Account Details
Bank: Habib Bank Limited
Account Title: AIN GenX
Account No: 5910-70000512-03
IBAN No: PK08 HABB 0059 1070 0005 1203
Secure a Verified Certificate from AIN GenX
Apply for Skill Development Council Certificate

Participants from Various  Companies 




















What do participants say about AIN GenX?
As a human resource professional, I'm enhancing my skills in data analysis and business intelligence with AIN Genx (PVT) Ltd. The program, led by Mr. Irfan Bakaly and Nooruddin Surani, is well-structured and covers a wide range of material. The platform provided is helpful for comprehending concepts like data analytics, visualization, dashboard tools, and transformation. Learning is continuous, and with commitment, success is inevitable. I highly recommend this course for those looking to advance their skills.
Humaira NafeesHuman Resources Business Partner
I commend the diverse content in the data analytics course, especially the practical Excel analysis and Al integration modules facilitated by Mr. Irfan Bakaly. The comprehensive approach, including R language and SQL sessions, is proving effective for my transition from Electrical Engineering. Exceptional instruction from Mr. Bakaly and Mr. Noor, coupled with additional resources access, ensures a supportive and confidence-building learning experience.
Engr. Abdul Basit Ahmed QureshiEngr
I would like to share my currently ongoing journey with AIN GenX which is great so far. Currently, I am enrolled in their certified data analyst course and the learning outcome has increased after the passage of every class because of very experienced and humble mentors like Noor sir and Irfan sir this course is very deep and detailed with full sound knowledge. in short, this course is highly recommended.
Faizan PervaizCoordinator at Bahria Town
It's just two months to this exciting journey of learning the data analyst course and so far, it has been an exhilarating experience with learning new skills in MS Excel and more is yet to be unlocked. Too excited to learn more in this six-month journey from amazingly talented mentors.
Farah NazAsst. Director Clinical Governance and Trainings
The Data Analyst course has been phenomenal! The mentors Mr. Irfan Bakaly and Mr.Noor Surani are exceptional, and the course content is simply amazing. The AIN GenX team's support and expertise are outstanding. With two months behind me, I am thrilled for the remaining four months of this journey!
Muhammad Shahzad Ahmed
AIN GenX course in Power BI and Python was incredibly beneficial. The hands-on experience and expert guidance have enhanced my data analysis skills significantly, making complex tasks seem simple. I highly recommend AIN GenX for anyone looking to excel in data analytics.
Noman SaeedShipping and Port Industry
